2 Search gene metadata
genInfo() function helps the user quickly search batch of gene metadata such as names, location, GC content, etc.
2.1 Supported organisms
It supports 195 vertebrate species, 120 plant species, and two bacteria species. All data is up-to-date.
# install.packages('DT')
library(genekitr)
DT::datatable(ensOrg_name, options = list(pageLength = 10))A user could select an organism name from the latin_short_name column.
The common name is also acceptable for popular research species (e.g., human, mouse, rat, fly, zebrafish, worm, chicken). Take human as an example, the official latin short name is “hsapiens”, while" hg“,”hsa“,”hs“, or”human" are also acceptable.
2.2 Basic usage
genInfo only has three arguments:
id: gene id (symbol, Entrez or Ensembl) or protein idorg: organism name, default is humanunique:TRUEorFALSE. Commonly, one gene could have many other types of matched records. For example, the humanHBDgene has three matched Entrez IDs: 3045, 85349, and 100187828. IfTRUE,only return a one-to-one match result with smallest entrezid or maximal information (that is minimal NAs). See example genekitr feature2.
## [1] "input_id" "symbol" "entrezid" "ensembl"
## [5] "uniprot" "chr" "start" "end"
## [9] "width" "strand" "gene_name" "ncbi_alias"
## [13] "ensembl_alias" "gc_content" "gene_biotype" "transcript_count"
## [17] "hgnc_id" "omim" "ccds" "reactome"
## [21] "ucsc" "mirbase_id" "cell_marker"head(info, 3)## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 1 TP53 TP53 7157 ENSG00000141510
## 2 BRCA1 BRCA1 672 ENSG00000012048
## 3 TET2 TET2 54790 ENSG00000168769
## uniprot chr
## 1 K7PPA8; P04637; Q53GA5; H2EHT1; A0A087X1Q1; A0A087WXZ1; A0A087WT22 17
## 2 P38398; A0A024R1V0 17
## 3 A0A158SIU0; Q6N021; A0A024RDF7 4
## start end width strand gene_name
## 1 7661779 7687538 25760 -1 tumor protein p53
## 2 43044295 43170245 125951 -1 BRCA1 DNA repair associated
## 3 105145875 105279816 133942 1 tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2
## ncbi_alias
## 1 BCC7; BMFS5; LFS1; P53; TRP53
## 2 BRCAI; BRCC1; BROVCA1; FANCS; IRIS; PNCA4; PPP1R53; PSCP; RNF53
## 3 IMD75; KIAA1546; MDS
## ensembl_alias gc_content gene_biotype transcript_count
## 1 LFS1; p53 48.85 protein_coding 27
## 2 BRCC1; FANCS; PPP1R53; RNF53 44.09 protein_coding 34
## 3 FLJ20032; KIAA1546 36.29 protein_coding 9
## hgnc_id omim
## 1 HGNC:11998 191170
## 2 HGNC:1100 113705
## 3 HGNC:25941 612839
## ccds
## 1 CCDS73967; CCDS73966; CCDS73968; CCDS73964; CCDS73965; CCDS73963; CCDS73969; CCDS45606; CCDS45605; CCDS73970; CCDS73971; CCDS11118
## 2 CCDS11453; CCDS11456; CCDS11455; CCDS11459; CCDS11454
## 3 CCDS3666; ; CCDS47120
## reactome
## 1 R-HSA-1643685; R-HSA-392499; R-HSA-597592; R-HSA-109582; R-HSA-168256; R-HSA-212436; R-HSA-2262752; R-HSA-73857; R-HSA-74160; R-HSA-8953897; R-HSA-162582; R-HSA-5688426; R-HSA-5689880; R-HSA-2990846; R-HSA-3108232; R-HSA-5693532; R-HSA-73894; R-HSA-109581; R-HSA-109606; R-HSA-114452; R-HSA-1257604; R-HSA-5357801; R-HSA-9006925; R-HSA-1640170; R-HSA-69278; R-HSA-69620; R-HSA-3700989; R-HSA-5633008; R-HSA-6803207; R-HSA-5218859; R-HSA-157118; R-HSA-6807070; R-HSA-8943724; R-HSA-983231; R-HSA-2559583; R-HSA-8853884; R-HSA-6796648; R-HSA-453274; R-HSA-69275; R-HSA-1912408; R-HSA-1912422; R-HSA-6803204; R-HSA-8878159; R-HSA-390466; R-HSA-390471; R-HSA-391251; R-HSA-1280215; R-HSA-449147; R-HSA-69481; R-HSA-6785807; R-HSA-2559580; R-HSA-2559585; R-HSA-349425; R-HSA-69541; R-HSA-69563; R-HSA-69580; R-HSA-69615; R-HSA-8852276; R-HSA-3232118; R-HSA-5693565; R-HSA-5693606; R-HSA-5633007; R-HSA-6804756; R-HSA-69473; R-HSA-9645723; R-HSA-5689896; R-HSA-8941855; R-HSA-2559586; R-HSA-5628897; R-HSA-6804757; R-HSA-6804759; R-HSA-6806003; R-HSA-6803211; R-HSA-5620971; R-HSA-6804754; R-HSA-6804758; R-HSA-139915; R-HSA-6803205; R-HSA-6791312; R-HSA-6804115; R-HSA-6804114; R-HSA-6804116; R-HSA-69560; R-HSA-69895; R-HSA-2559584; R-HSA-6804760; R-HSA-6811555; R-HSA-111448; R-HSA-9723905; R-HSA-9723907
## 2 R-HSA-1643685; R-HSA-392499; R-HSA-597592; R-HSA-212436; R-HSA-73857; R-HSA-74160; R-HSA-5688426; R-HSA-2990846; R-HSA-3108214; R-HSA-3108232; R-HSA-5685938; R-HSA-5693532; R-HSA-5693538; R-HSA-5693567; R-HSA-73894; R-HSA-1640170; R-HSA-69620; R-HSA-3700989; R-HSA-6796648; R-HSA-69481; R-HSA-5693565; R-HSA-5693606; R-HSA-1474165; R-HSA-1221632; R-HSA-1500620; R-HSA-5633007; R-HSA-5685942; R-HSA-5689901; R-HSA-5693537; R-HSA-5693554; R-HSA-5693568; R-HSA-5693571; R-HSA-5693579; R-HSA-5693607; R-HSA-5693616; R-HSA-6804756; R-HSA-69473; R-HSA-8953750; R-HSA-912446; R-HSA-9663199; R-HSA-9675135; R-HSA-9675136; R-HSA-9699150; R-HSA-9701193; R-HSA-9704331; R-HSA-9704646
## 3 R-HSA-74160; R-HSA-212165; R-HSA-5221030
## ucsc
## 1 uc002gig.2; uc284ohw.1; uc002gih.5; uc060auo.1; uc060aup.1; uc060auq.1; uc010cnf.2; uc010cng.2; uc002gii.2; uc031qyq.2; uc002gij.4; uc060aus.1; uc060aut.1; uc010cnh.4; uc060auu.1; uc060auv.1; uc060aur.2; uc002gim.5; uc060auw.1; uc060auy.1; uc060auz.1; uc010cnj.2; uc060ava.1; uc060avb.1; uc060avc.1; uc060avd.1; uc032esw.2
## 2 uc060fri.1; uc002icq.6; uc002ict.5; uc002icu.4; uc285oaj.1; uc010whm.3; uc010whn.3; uc060frj.1; uc010cyx.4; uc060frk.1; uc060frl.1; uc060frm.1; uc060frn.1; uc060fro.1; uc060frp.1; uc060frq.1; uc060frr.1; uc060frs.1; uc002idd.5; uc284oig.1; uc060frt.1; uc060fru.1; uc287jed.1; uc060frv.1; uc060frw.1; uc060frx.1; uc060fry.1; uc060frz.1; uc285oak.1; uc060fsa.1; uc060fsb.1; uc060fsc.1; uc285oal.1; uc060fsd.1
## 3 uc021xqk.1; uc011cez.3; uc062ysb.1; uc003hxj.3; uc003hxk.5; uc062ysc.1; uc010ilp.3; uc062yse.1; uc062ysf.1
## mirbase_id
## 1 <NA>
## 2 <NA>
## 3 <NA>
## cell_marker
## 1 Fetal gonad|T|Mitotic fetal germ cell; Fetal gonad|T|Gonadal endothelial cell; Fetal kidney|T|Natural killer T (NKT) cell; Fetal gonad|N|Mitotic fetal germ cell; Fetal gonad|N|Gonadal endothelial cell; Fetal kidney|N|Natural killer T (NKT) cell
## 2 Fetal kidney|T|Natural killer T (NKT) cell; Fetal kidney|N|Natural killer T (NKT) cell
## 3 Embryo|T|Trophectoderm cell; Liver|T|Exhausted CD8+ T cell; Liver|T|Regulatory T (Treg) cell; Fetal kidney|T|Natural killer T (NKT) cell; Embryo|N|Trophectoderm cell; Liver|T|Exhausted CD8+ T cell; Liver|T|Regulatory T (Treg) cell; Fetal kidney|N|Natural killer T (NKT) cell2.3 Features
2.3.1 f1: keep input order
genInfo result will strictly keep up with the input order.
If a gene id is unrecognized (e.g., misspelled or does not belong to the organism), the return data will be NA.
id <- c(
"MCM10", "CDC20", "S100A9",
"FAKEID", "TP53", "HBD", "NUDT10"
)
# for human id, no need to input the org argument
info <- genInfo(id, unique = TRUE)
identical(id, info$input_id)## [1] TRUEhead(info, 3)## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl uniprot chr start end
## 1 MCM10 MCM10 55388 ENSG00000065328 Q7L590 10 13161558 13211110
## 2 CDC20 CDC20 991 ENSG00000117399 Q12834 1 43358981 43363203
## 3 S100A9 S100A9 6280 ENSG00000163220 P06702 1 153357854 153361023
## width strand gene_name
## 1 49553 1 minichromosome maintenance 10 replication initiation factor
## 2 4223 1 cell division cycle 20
## 3 3170 1 S100 calcium binding protein A9
## ncbi_alias
## 1 CNA43; DNA43; IMD80; PRO2249
## 2 CDC20A; bA276H19.3; p55CDC
## 3 60B8AG; CAGB; CFAG; CGLB; L1AG; LIAG; MAC387; MIF; MRP14; NIF; P14; S100-A9
## ensembl_alias
## 1 CNA43; DNA43; PRO2249
## 2 CDC20A; p55CDC
## 3 60B8AG; CAGB; CFAG; CGLB; LIAG; MAC387; MIF; MRP-14; MRP14; NIF; P14; S100-A9
## gc_content gene_biotype transcript_count hgnc_id omim
## 1 43.59 protein_coding 7 HGNC:18043 609357
## 2 52.17 protein_coding 4 HGNC:1723 603618
## 3 52.56 protein_coding 1 HGNC:10499 123886
## ccds
## 1 CCDS7095; ; CCDS7096
## 2 CCDS484
## 3 CCDS1036
## reactome
## 1 R-HSA-1640170; R-HSA-69278; R-HSA-69620; R-HSA-69306; R-HSA-176187; R-HSA-453279; R-HSA-68962; R-HSA-69002; R-HSA-69206; R-HSA-69481
## 2 R-HSA-392499; R-HSA-597592; R-HSA-168256; R-HSA-162582; R-HSA-194315; R-HSA-195258; R-HSA-5688426; R-HSA-5689880; R-HSA-9716542; R-HSA-1280218; R-HSA-141424; R-HSA-141444; R-HSA-1640170; R-HSA-2467813; R-HSA-2500257; R-HSA-2555396; R-HSA-5663220; R-HSA-68877; R-HSA-68882; R-HSA-68886; R-HSA-69278; R-HSA-69618; R-HSA-69620; R-HSA-9648025; R-HSA-983168; R-HSA-983169; R-HSA-141405; R-HSA-141430; R-HSA-174048; R-HSA-174143; R-HSA-174154; R-HSA-174178; R-HSA-174184; R-HSA-176407; R-HSA-176408; R-HSA-176409; R-HSA-176814; R-HSA-179409; R-HSA-179419; R-HSA-453276; R-HSA-174113; R-HSA-176417
## 3 R-HSA-1643685; R-HSA-168249; R-HSA-168256; R-HSA-6798695; R-HSA-162582; R-HSA-194315; R-HSA-195258; R-HSA-9716542; R-HSA-1280218; R-HSA-983169; R-HSA-166016; R-HSA-168898; R-HSA-5668599; R-HSA-1236974; R-HSA-1236975; R-HSA-6803157; R-HSA-166058; R-HSA-168179; R-HSA-168188; R-HSA-181438; R-HSA-5260271; R-HSA-5602358; R-HSA-5602498; R-HSA-5603041; R-HSA-6799990; R-HSA-5686938
## ucsc
## 1 uc001imb.4; uc057rtn.1; uc001ima.4; uc057rto.1; uc057rtp.1; uc057rtq.1; uc057rtr.1
## 2 uc001cix.5; uc001ciy.4; uc057fmt.1; uc057fmu.1
## 3 uc001fbq.4
## mirbase_id
## 1 <NA>
## 2 <NA>
## 3 <NA>
## cell_marker
## 1 Fetal gonad|T|Migration phase fetal germ cell; Umbilical cord blood|T|Granulocyte-monocyte progenitor; Fetal gonad|N|Migration phase fetal germ cell; Umbilical cord blood|N|Granulocyte-monocyte progenitor
## 2 Embryonic prefrontal cortex|T|Neural progenitor cell; Muscle|T|Myoblast; Large intestine|T|MKI67+ progenitor cell; Embryonic prefrontal cortex|N|Neural progenitor cell; Muscle|N|Myoblast; Large intestine|N|MKI67+ progenitor cell
## 3 Small intestine|T|Enterocyte progenitor cell; Fetal gonad|T|Granulosa cell; Blood|T|CD1C+_B dendritic cell; Fetal kidney|T|Monocyte; Kidney|T|Neutrophil; Kidney|T|Plasma cell; Kidney|T|Neutrophil; Undefined|N|Eosinophil; Undefined|N|Neutrophil; Bone marrow|N|Monocyte derived dendritic cell; Small intestine|N|Enterocyte progenitor cell; Fetal gonad|N|Granulosa cell; Blood|N|CD1C+_B dendritic cell; Fetal kidney|N|Monocyte; Kidney|N|Neutrophil; Kidney|T|Plasma cell; Kidney|T|Neutrophil2.3.2 f2: keep unique or not
If unique = TRUE, only one record with maximal information is returned.
id <- "HBD"
uniq_info <- genInfo(id, org = "hs", unique = TRUE)
uniq_info[, 1:4]## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 2 HBD HBD 3045 ENSG00000223609all_info <- genInfo(id, org = "hs", unique = FALSE)
all_info[, 1:4]## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 1 HBD HBD 100187828 ENSG00000223609
## 2 HBD HBD 3045 ENSG00000223609
## 3 HBD KRT87P 85349 ENSG000001354772.3.3 f3: disambiguation feature
2.3.3.1 distinguish from gene symbol and alias
Many common gene names are gene alias, but many tools only accept gene symbols which cause gene information to be lost. For example, “BCC7” is the alias of “TP53” and “PD1” has three aliases: “PDCD1”, “SNCA” and “SPATA2” while few enrichment analyses tools recognize “BCC7”.
## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 1 BCC7 TP53 7157 ENSG00000141510
## 2 PD1 PDCD1 5133 ENSG00000276977
## 3 PD1 PDCD1 5133 ENSG00000188389
## 4 PD1 SNCA 6622 ENSG00000145335
## 5 PD1 SPATA2 9825 ENSG000001584802.3.3.2 distinguish gene symbol with special characters
## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 1 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000228978
## 2 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000228321
## 3 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000232810
## 4 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000204490
## 5 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000230108
## 6 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000223952
## 7 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000206439
## 8 TNF-α TNF 7124 ENSG00000228849
## 9 κB-Ras2 NKIRAS2 28511 ENSG000001682562.3.4 f4: count organism gene types
org <- "hs"
uniq_symbol <- genInfo(org = org) %>%
dplyr::filter(!is.na(gene_biotype)) %>%
dplyr::distinct(symbol, .keep_all = T)
uniq_symbol %>%
{
table(.$gene_biotype)
}##
## IG_C_gene IG_C_pseudogene
## 14 9
## IG_D_gene IG_J_gene
## 37 18
## IG_J_pseudogene IG_V_gene
## 3 144
## IG_V_pseudogene Mt_rRNA
## 184 2
## Mt_tRNA TEC
## 23 27
## TR_C_gene TR_D_gene
## 7 4
## TR_J_gene TR_J_pseudogene
## 79 4
## TR_V_gene TR_V_pseudogene
## 107 33
## lncRNA miRNA
## 6095 1852
## misc_RNA polymorphic_pseudogene
## 1034 49
## processed_pseudogene protein_coding
## 7199 19572
## rRNA rRNA_pseudogene
## 46 496
## ribozyme sRNA
## 4 1
## scRNA scaRNA
## 1 18
## snRNA snoRNA
## 1833 437
## transcribed_processed_pseudogene transcribed_unitary_pseudogene
## 355 132
## transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene translated_processed_pseudogene
## 770 2
## translated_unprocessed_pseudogene unitary_pseudogene
## 2 78
## unprocessed_pseudogene
## 17062.3.5 f5: extract all metadata
If user only wants to get all information, just give org argument alone.
## [1] 92441 222.3.6 f6: extract specific biotype genes
2.3.6.0.1 Get all human protein-coding genes:
hg_pro_gene <- uniq_symbol %>%
dplyr::filter(gene_biotype == "protein_coding") %>%
dplyr::pull(symbol)
length(hg_pro_gene)## [1] 195722.3.6.0.2 Compare with HGNC data:
hgnc_data <- vroom::vroom("http://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/genenames/hgnc/tsv/locus_types/gene_with_protein_product.txt")
hgnc_symbol <- hgnc_data$symbol
plotVenn(list(
genekitr_symbol = hg_pro_gene,
hgnc_symbol = hgnc_symbol
))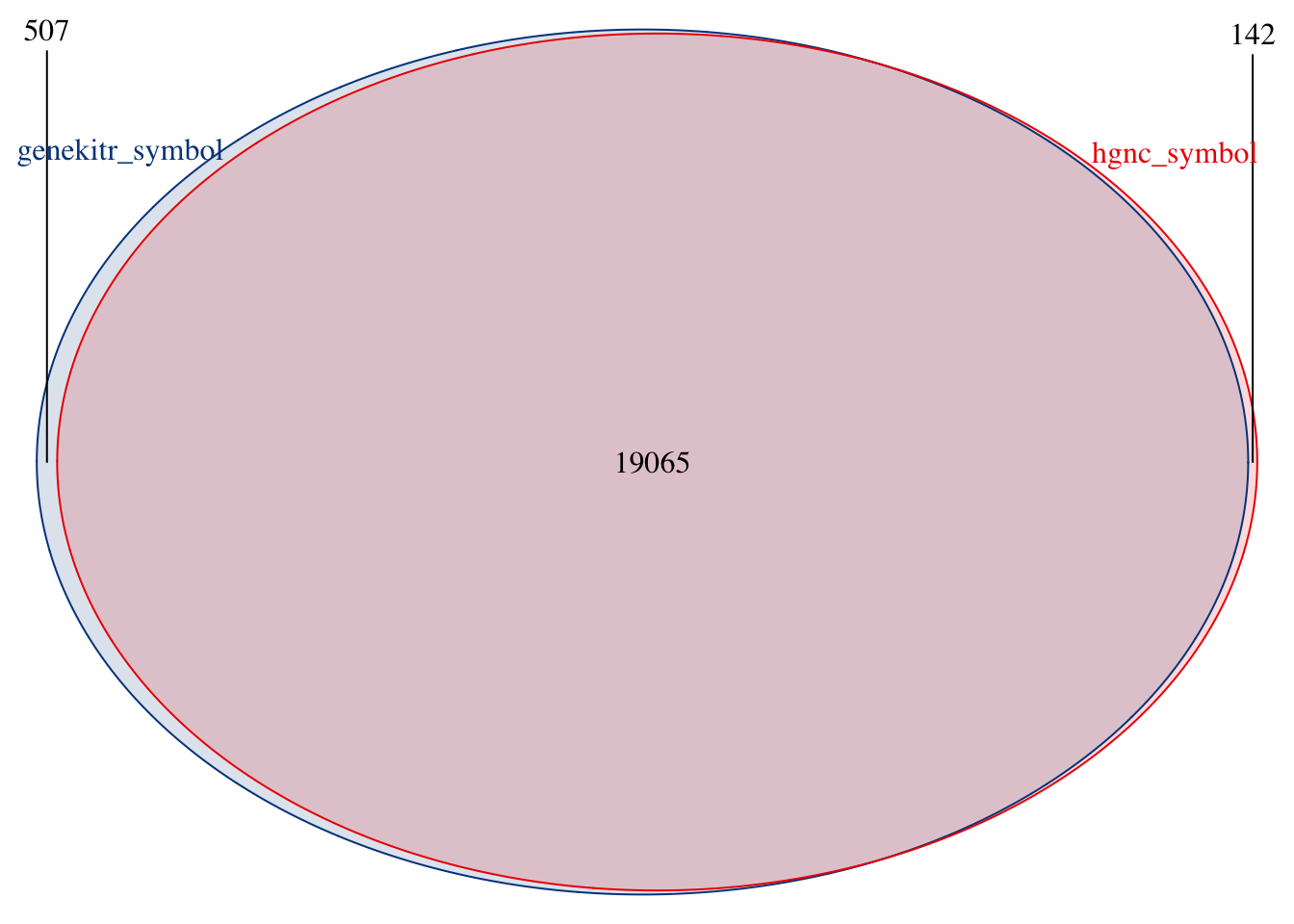
Check some missing gene names in our result:
check_genes <- head(hgnc_symbol[!hgnc_symbol %in% hg_pro_gene], 3)
hgnc_data %>%
dplyr::filter(symbol %in% check_genes) %>%
dplyr::select(
symbol, date_approved_reserved, date_symbol_changed,
entrez_id
)## symbol date_approved_reserved date_symbol_changed entrez_id
## 1 ABTB3 2003-12-15 2022-05-13 121551
## 2 ADGRF2 2002-11-26 2015-03-03 222611
## 3 AKR7L 2008-12-09 <NA> 246181Let’s look at the first one “ABTB3”:
It seems that the gene “ABTB3” is recently modified, while it is also known as “BTBD11” which matched with our Ensembl data: ENSG00000151136
genInfo("121551")[1:3]## input_id ensembl symbol
## 1 121551 ENSG00000151136 BTBD11So the reason for the mismatch is out-of-sync of the large database Ensembl and NCBI. However, the mismatch number is small so the effect is not serious.
Here is my personal view:
NCBI updates backend data everydata while Ensembl follows a quarterly update cycle.
As long as our genes are not so outdated, it can also finish gene annotation such as enrichment analysis. It is not recommended to keep gene names updated like NCBI because other large databases could not follow a very high updating frequency.
For example, the gene “BTBD11” (BTB/POZ domain-containing protein 11) could be recognized in GeneOntology while the latest one “ABTB3” is not synced yet. If using NCBI name, user may not get related enrichment information about this gene.
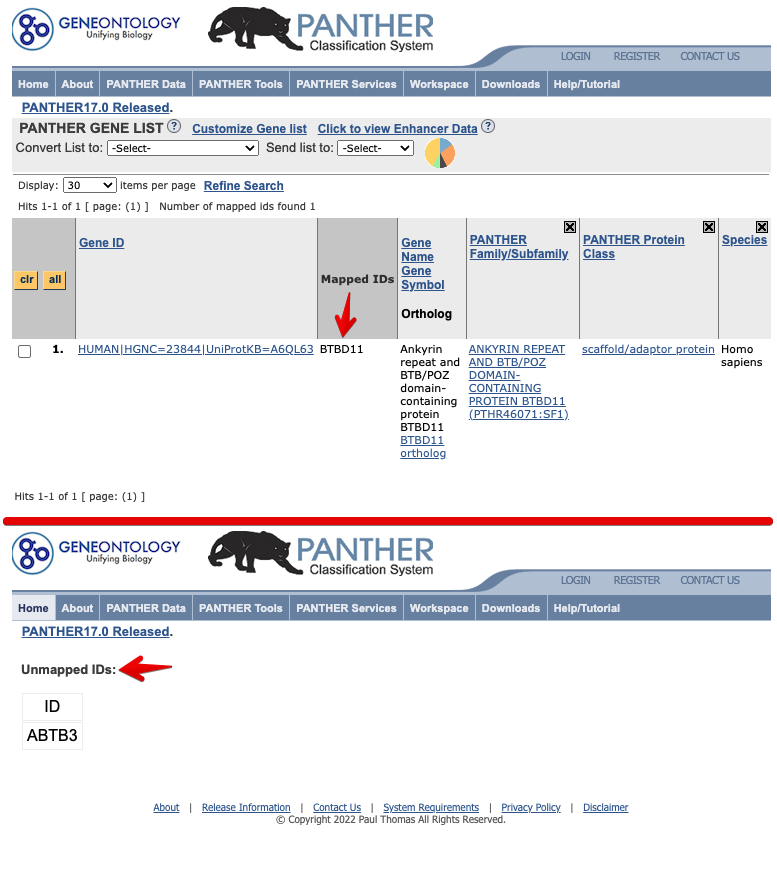
Figure 2.1: BTBD11 vs ABTB3 in GeneOntology
2.3.6.0.3 Compare with orgDb in Bioconductor
Because genekitr combines both Ensembl and NCBI data, it could handle more gene ids than common organism-level (‘org’) packages in Bioconductor.
# using orgdb
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
org_dat = AnnotationDbi::select(org.Hs.eg.db,
keys = AnnotationDbi::keys(org.Hs.eg.db),
keytype = 'ENTREZID',
columns = 'SYMBOL')
org_sym <- unique(org_dat$SYMBOL)
length(org_sym)## [1] 61538## [1] 66229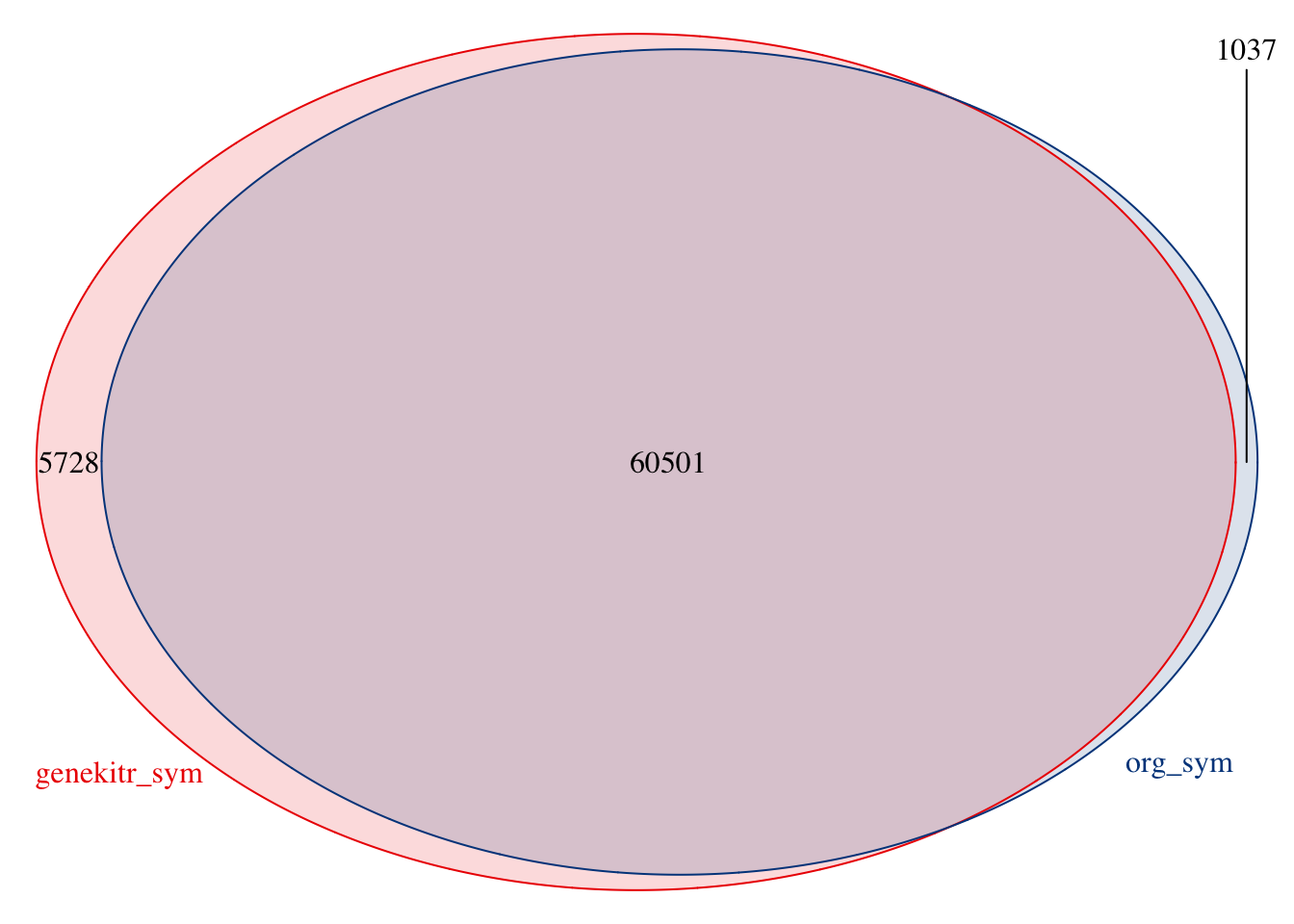
Some genes only exist in genekitr:
## [1] "SPDYE12" "MCTS2" "NAV2-AS6" "SLC66A2P2" "ARHGAP44-AS1"
## [6] "PHB1P16"genInfo("SPDYE12")[1:4]## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 1 SPDYE12 SPDYE12 100101268 ENSG00000184616For example, gene 100101268 is officially named as SPDYE12, while in orgdb the name is:
org_dat[org_dat$ENTREZID=="100101268","SYMBOL"]## [1] "SPDYE12P"Do not worry, if you use genekitr, you can still get exact match:
genInfo("SPDYE12P")[1:4]## input_id symbol entrezid ensembl
## 1 SPDYE12P SPDYE12 100101268 ENSG000001846162.3.7 f7: extract human cell markers
CellMarker database has manually curated over 100,000 published papers, 4,124 entries including the cell marker information, tissue type, cell type, cancer information and source.
Here, geneInfo integrated human cell markers into cell_marker column.
The naming rules is: tissue_type | cancer_type: Tumor(T) or Normal(N) | cell_type, if one gene matches many cell types, they are seperated with ;.
hg_marker_all <- genInfo(org = "human") %>%
dplyr::select(symbol, cell_marker) %>%
dplyr::filter(!is.na(cell_marker)) %>%
tidyr::separate_rows(cell_marker, sep = "; ") %>%
dplyr::mutate(cell_marker = gsub("^.*\\|", "", cell_marker)) %>%
dplyr::distinct()
head(hg_marker_all)## # A tibble: 6 × 2
## symbol cell_marker
## <chr> <chr>
## 1 A1BG Retinoid acid signaling-responsive fetal germ cell
## 2 ADA Brush cell (Tuft cell)
## 3 ADA Neuroendocrine cell
## 4 ADA Retinoid acid signaling-responsive fetal germ cell
## 5 ADA Oogenesis phase fetal germ cell
## 6 ADA Mitotic arrest phase fetal germ cell# select stromal cell markers
hg_marker_all %>%
dplyr::filter(cell_marker == "Stromal cell") %>%
dplyr::pull(symbol) %>%
sort()## [1] "ALCAM" "ANPEP" "BST1" "CD34" "CD44" "COL5A1" "ENG"
## [8] "GREM1" "ICAM1" "ICAM2" "ICAM3" "ITGA1" "ITGA4" "ITGAV"
## [15] "ITGB1" "ITGB3" "KIT" "KLF6" "LTBR" "LUM" "MADCAM1"
## [22] "MCAM" "MME" "MMP1" "MMP2" "MMP9" "NGFR" "NT5E"
## [29] "PDGFRA" "PDGFRB" "PDPN" "PECAM1" "PROM1" "PTPRC" "THY1"
## [36] "TIMP1" "TIMP2" "TLR1" "TLR2" "TLR3" "TLR4" "VCAM1"
## [43] "VIM"